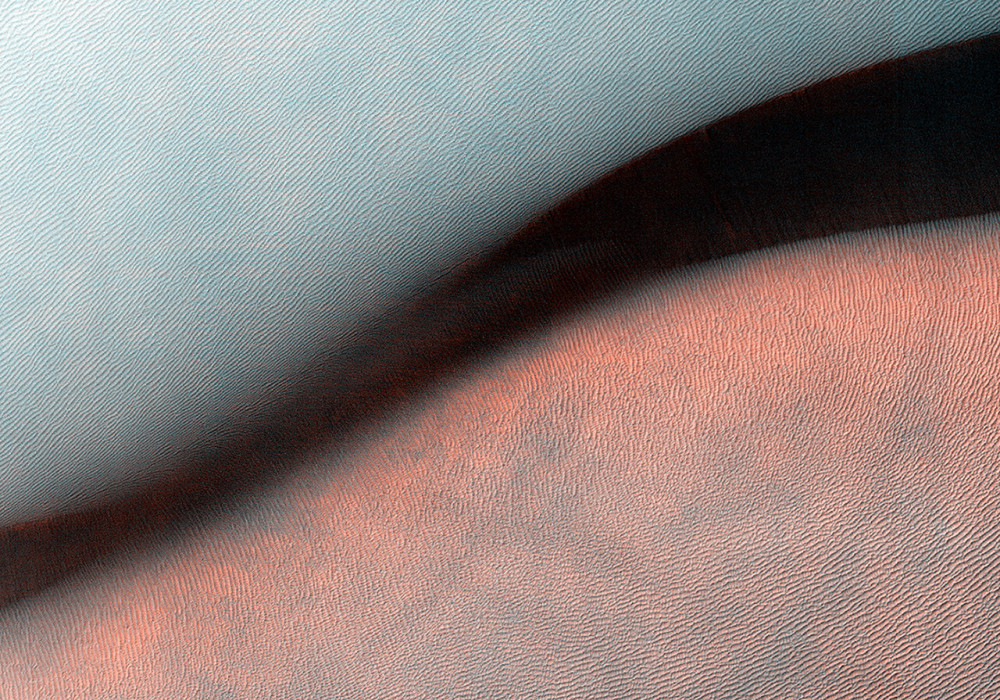
Sandy landforms formed by the wind or aeolian bedforms are classified by the wavelength—or length—between crests. On Mars we can observe four classes of bedforms (in order of increasing wavelengths): ripples, transverse aeolian ridges (known as TARs), dunes, and what are called “draa.” All of these are visible in this Juventae Chasma image.
Ripples are the smallest bed forms (less than 20 meters) and can only be observed in high-resolution images acquired by HiRISE commonly superposed on many surfaces . TARs are slightly larger bedforms (wavelengths approximately 20 to 70 meters), which are often light in tone relative to their surroundings. Dark-toned dunes (wavelengths 100 meters to 1 kilometer) are a common landform and many are active today. What geologists call “draa” is the highest-order bedform with largest wavelengths ( greater than 1 kilometer), and is relatively uncommon on Mars.
Here, this giant draa possess steep faces or slip faces several hundreds of meters tall and has lower-order superposed bedforms, such as ripples and dunes. A bedform this size likely formed over thousands of Mars years, probably longer.
Written by: Matthew Chojnacki (4 June 2014)
More info and image formats at http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_034909_1755
Image: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona